Introduction
Brief overview of the article's purpose and content
Introduction to EE, EF, EFD, and ETD bobbins
EE Bobbin
Definition and characteristics
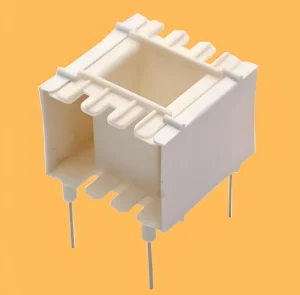
EE bobbins are one of types of transformer bobbin characterized by their distinctive E core and two separate halves, typically made of plastic or other insulating materials. The “E” shape allows for efficient winding of coils and ensures optimal magnetic flux distribution within the transformer. These bobbins often feature symmetrical legs and a central divider, providing stability and support for the winding process.
Primary uses and applications
EF Bobbin
Definition and characteristics
Primary uses and applications
EFD Bobbin
Definition and characteristics
Primary uses and applications
ETD Bobbin
Definition and characteristics
ETD bobbins feature an E-shaped core with a center post on one end and a flange on the other, distinguishing them as a specialized type of transformer bobbin. This configuration enables efficient coil winding and structural support, ideal for high-frequency applications. The center post increases winding space and enhances heat dissipation, while the flange ensures stability and ease of assembly.